Actin Fibers Are Involved in Which of the Following Processes
The actin cytoskeleton is a complex network of polarized filaments that is involved in many essential processes including motility and cytokinesis tumor cell transformation 2 and metastasis 39. If actin binding sites are covered and unavailable the myosin will remain in the high energy configuration with ATP hydrolyzed but still attached.
The Cell 7 Cytoskeleton Actin Filaments Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
Therefore Vincristine will not affect muscle contraction.

. By kymograph analysis we found median fiber velocities in the range of 02 μmmin with a weak dependence on pattern width. They commonly underlie the plasma membrane and are typically assembled at the cell periphery from adhesion sites or. If the actin binding sites are uncovered a cross-bridge will form.
Fiber dynamics was characterized by a directed movement from the cell edges towards the cell center where fiber dissolution frequently took place. Myosin releases the ADP molecule. Actin filaments are involved in which of the following processes.
ATP-driven pumps will move Ca out of the sarcoplasm back into the SR. A contractile cytoskeleton in podocytes and mesangial cells formed by F-actin-containing stress fibers maintains structural integrity and modulates glomerular. The thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that the actin and myosin myofilaments overlap to a greater degree.
The ATP is again hydrolyzed and last four steps of the process are repeated making the sarcomere shorter and shorter until adequate Ca and ATP are present. In which of the following processes is the cytoskeleton involved. Forces acting on the actin cytoskeleton are translated and transmitted by signaling pathways to convey.
Myosin head bends and actin slides over the myosin surface. Some keys functions are. They pull on actin filaments which move toward the center of the sarcomere causing contraction.
To form the dynamic cytoskeleton which gives structural support to cells and links the interior of the cell with its surroundings. Although not directly involved in the contractile machinery the microtubular network is involved. The two proteins directly involved in muscle contraction are broadly called _____.
Which of the following processes will be unaffected in cells treated with cytochalasin D. Also actin filaments provide structural support and have a role in determining cell shape. Relaxing skeletal muscle fibers and ultimately the skeletal muscle begins with the motor neuron which stops releasing its chemical signal ACh into the synapse at the NMJ.
The cytoskeletal element is involved in cell movement and. Several biological processes related to cell shape and movement depend on actin filaments reviewed in 1. Stress fibers composed of actin filaments and myosin II motors and cell adhesion sites on which stress fibers are anchored.
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers in the cytoplasm that give. Up to 10 cash back Actin-myosin interactions involved in muscle contraction do not depend on the microtubules. Which of the following is likely to be a symptom.
Actin filaments usually in association with myosin are responsible for many types of cell movements. Resulting in the loss of ACh receptors at the motor end plate of muscle fibers. Actin Myosin and Cell Movement - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf.
Formation of contractile ring during cytokinesis. Actin filaments F-actin are linear polymers of globular actin G-actin subunits and occur as microfilaments in the cytoskeleton and as thin filaments which are part of the contractile apparatus in muscle and nonmuscle cells see contractile bundles. This step sees the formation of an actin nucleus which is essentially a complex of three actin monomers from which an actin filament may elongate.
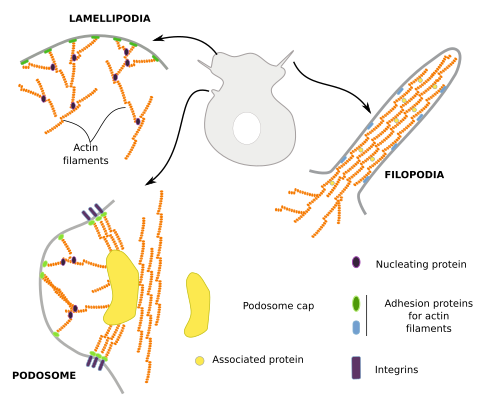
Glomerular distention is associated with cellular mechanical strain. Formation of lamellipodium and filopodium. The small GTPase Rho promotes the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions leading to increased contractility Figure 2.
Actin fibers are involved in which of the following processes a Pseudopod from SC 166 at Herzing University. Actin filaments are involved in which of the following processes. As the myosin head swivels another ATP molecule binds to myosin breaking the actin-myosin bridge.
Although non-muscle cells have a high concentration of G-actin-ATP 100 μM 1 pure G-actin monomers fail to nucleate new actin filaments efficiently due to the. A cytoplasmic streaming B contraction of muscle fibers C extension of pseudopodia D movement of. Formation of cell cortex.
The muscle fiber will repolarize which closes the gates in the SR where Ca was being released. Myosin is the prototype of a molecular motora protein that converts chemical energy in the form of ATP to mechanical energy thus generating force and movement. Microtubules form the mitotic spindle and comprise cilia and flagella.
Cytochalasin D is a drug that prevents actin polymerization. Taken together these data suggest that cell geometry determines actin. They are also the freeways on which motor proteins move and transport vesicles throughout the cell.
The first step in actin polymerization is known as nucleation. Microtubules The mitotic spinde organelle positioning vesicle movement cilia and flagellum are all reliant on this kind of cytoskeletal fiber. Formation of lamellipodium and filopodium Formation of cell cortex Formation.
That is the myosin head spans the. Actin filaments brace cells against surfaces and allow contractions in striated muscle. Contractile ring formed during cytokinesis.
In addition glomerular distentioncontraction is assumed to influence the filtration rate through changes in filtration surface area. Which of the following properties is unique to a particular cytoskeletal element either actin fibers microtubules or intermediate filaments. Actin fibers are involved with which type of movement.
Which of the following proteins form a complex that nucleates assembly of an actin filament at the end so that growth occurs rapidly from the end. The subunits of the cytoskeletal element bind to nucleotides. The fully assembled cytoskeletal element exhibits polarity.

How Do Actin Filaments Depolymerize Mbinfo

Actin Cytoskeleton Flashcards Quizlet

How Are Actin Filaments Distributed In Cells And Tissues Mbinfo
No comments for "Actin Fibers Are Involved in Which of the Following Processes"
Post a Comment